Introduction
Welcome to denzidesign.com In today’s digital world, high-quality video transmission is essential for everything from professional workstations to home entertainment setups. With numerous video connection standards available, understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions. One such standard that has been widely used over the years is the Digital Visual Interface (DVI).
DVI was developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG) in 1999 as a successor to the analog VGA (Video Graphics Array) standard. It served as an important stepping stone between traditional analog connections and modern digital interfaces like HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) and DisplayPort. Designed to support both analog and digital signals, DVI played a significant role in the transition to high-definition displays, especially in computer monitors, projectors, and older HDTVs.
Although newer technologies such as HDMI and DisplayPort have largely replaced DVI, it is still found in many legacy systems, gaming setups, and professional environments where high-resolution, high-refresh-rate displays are necessary. In this blog, we’ll explore everything you need to know about DVI, including its different types, advantages, limitations, and comparisons with other video interfaces.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of whether DVI is still relevant for your needs and how it compares to HDMI and DisplayPort. Let’s dive in!
What is Digital Visual Interface (DVI)?
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display standard developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG) to transmit high-quality video signals. It serves as a bridge between older analog connections like VGA and newer digital standards like HDMI and DisplayPort.
DVI is commonly found in computer monitors, projectors, and older HDTVs, providing clear and sharp images for various applications, including gaming, video editing, and professional displays.
Types of DVI Connectors
DVI connectors are classified into three main types:
1. DVI-D (Digital Only)
- Transmits digital signals only.
- Best for LCD and LED monitors.
- Supports resolutions up to 2560×1600 (dual-link).
2. DVI-A (Analog Only)
- Transmits only analog signals.
- Compatible with older CRT monitors.
- Not commonly used today.
3. DVI-I (Integrated Digital and Analog)
- Supports both digital and analog signals.
- Compatible with various display types.
- Offers flexibility for mixed digital and analog setups.
Additionally, DVI connectors are available in two bandwidth types:
- Single-Link DVI: Supports resolutions up to 1920×1200 at 60Hz.
- Dual-Link DVI: Provides higher bandwidth, supporting up to 2560×1600 at 60Hz.
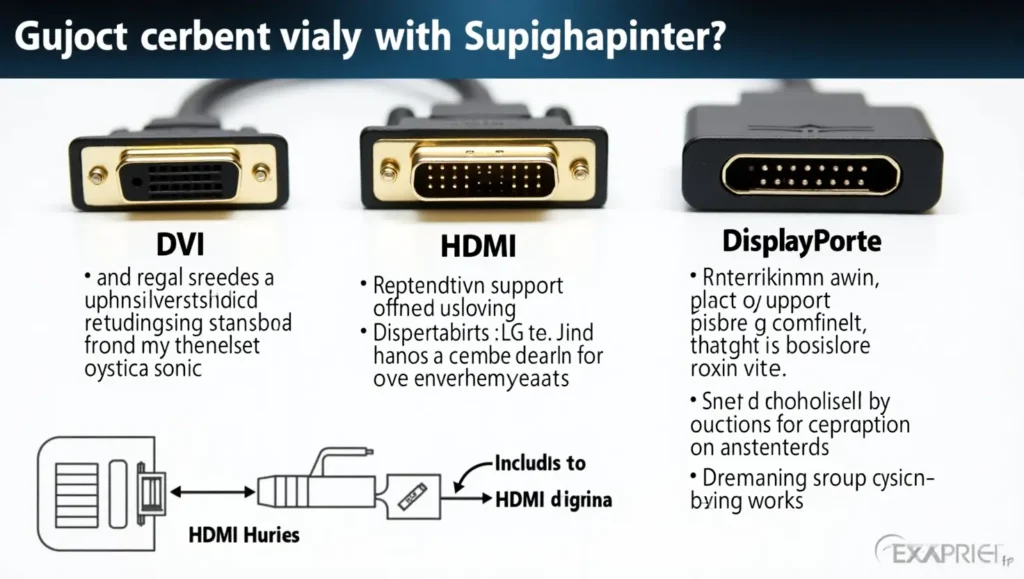
DVI vs. HDMI vs. DisplayPort
DVI vs. HDMI
| Feature | DVI | HDMI |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Digital/Analog | Digital (Video + Audio) |
| Audio Support | No | Yes |
| Maximum Resolution | 2560×1600 (dual-link) | 4K and beyond |
| Best Use Case | PC Monitors | TVs, Consoles, Modern Displays |
DVI lacks audio support and higher resolutions, making HDMI a better choice for modern multimedia setups.
DVI vs. DisplayPort
| Feature | DVI | DisplayPort |
| Signal Type | Digital/Analog | Digital (Video + Audio) |
| Audio Support | No | Yes |
| Maximum Resolution | 2560×1600 | 8K and beyond |
| Adaptive Sync | No | Yes (G-Sync, FreeSync) |
DisplayPort is the superior option for high refresh rate gaming and multi-monitor setups.
How to Convert DVI to HDMI and DisplayPort
Since DVI lacks audio transmission and support for modern resolutions, adapters and cables help users connect DVI devices to HDMI or DisplayPort screens.
- DVI to HDMI Adapter/Cable: Converts video signals only; requires separate audio cable.
- DisplayPort to DVI Adapter: Used for older monitors with only DVI ports.
Using active adapters ensures signal compatibility when switching between different video interfaces.
When Should You Use DVI?
While DVI is becoming obsolete, it’s still a reliable option in specific scenarios:
- Legacy Systems: Older desktops and monitors that don’t support HDMI or DisplayPort.
- Professional Displays: Some high-end monitors still feature DVI for color accuracy and sharpness.
- Gaming (with Dual-Link DVI): Supports 144Hz at 1080p, making it a good choice for budget gamers.
For modern applications, however, HDMI and DisplayPort provide better performance and future-proofing.
Conclusion
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) played a key role in transitioning from analog to digital video signals, offering clear, high-resolution images. However, with the rise of HDMI and DisplayPort, DVI is becoming less common. If you’re working with older devices, DVI to HDMI or DisplayPort adapters can help maintain compatibility.
Call to Action
Do you still use DVI for your setup? Let us know in the comments below! For more tech insights, subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated on the latest trends in digital connectivity.